Soil is one of the most important natural resources. It supports the growth of plants by holding the roots firmly and supplying water and nutrients. It is the home for many organisms. Soil is essential for agriculture. Agriculture provides food, clothing and shelter for all. Soil is thus an inseparable part of our life. The earthy fragrance of soil after the first rain is always refreshing.
SOIL PROFILE
- Soil is composed of distinct layers.
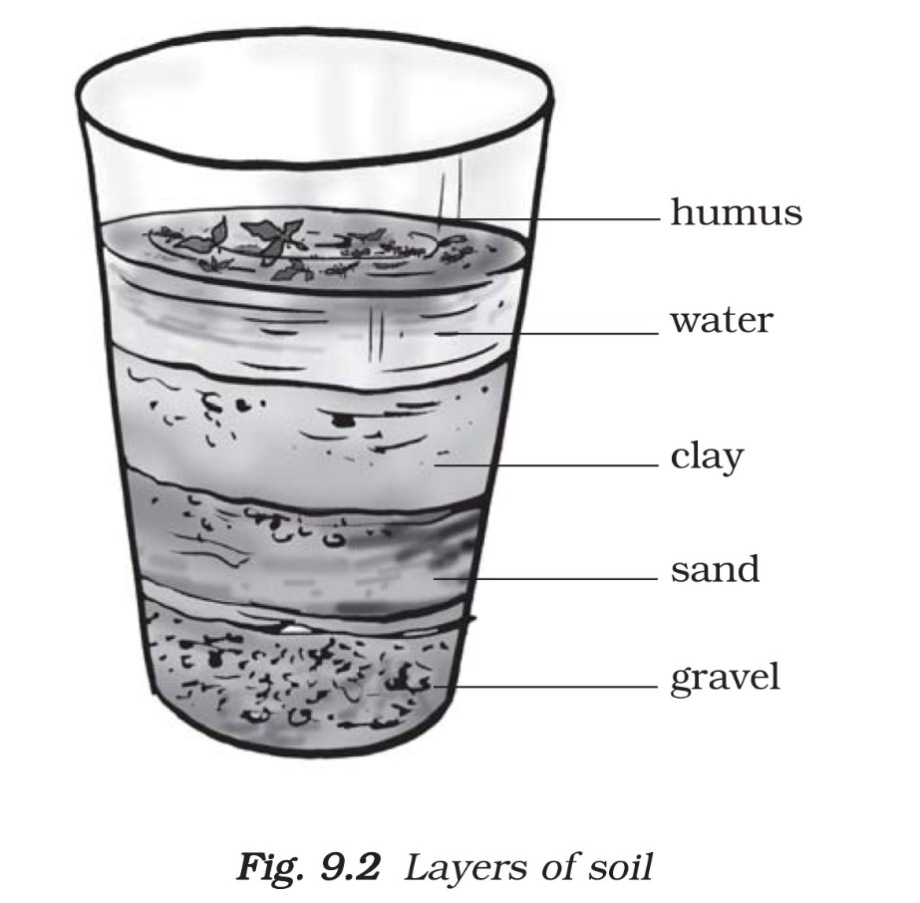
- Perform the following activity to find out how these layers are arranged. Take a little soil. Break the clumps with your hand to powder it. Now take a glass tumbler, three quarters filled with water, and then add a handful of soil to it. Stir it well with a stick to dissolve the soil. Now let it stand undisturbed for some time
- The rotting dead matter in the soil is called humus.
- You probably know that the soil is formed by the breaking down of rocks by the action of wind, water and climate. This process is called weathering.
- The nature of any soil depends upon the rocks from which it has been formed and the type of vegetation that grows in it.
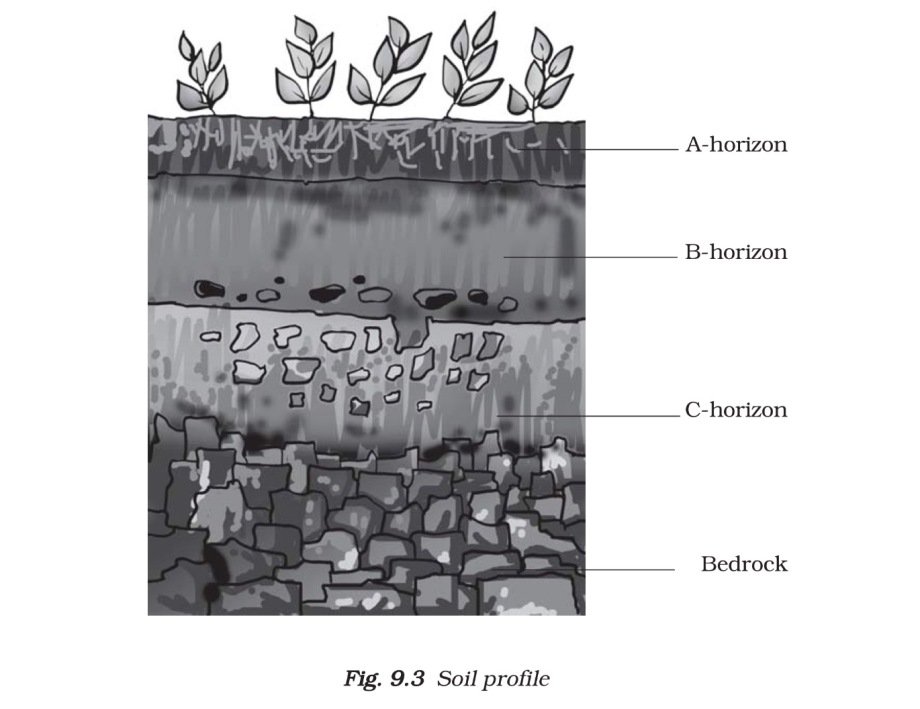
- A vertical section through different layers of the soil is called the soil profile. Each layer differs in feel (texture).
- These layers are referred to as horizons .
- We usually see the top surface of the soil, not the layers below it. If we look at the sides of a recently dug ditch, we can see the inner layers of the soil, too. Such a view enables us to observe the soil profile at that place.
- Soil profile can also be seen while digging a well or laying the foundation of a building. It can also be seen at the sides of a road on a hill or at a steep river bank.
- The uppermost horizon is generally dark in colour as it is rich in humus and minerals. The humus makes the soil fertile and provides nutrients to growing plants. This layer is generally soft, porous and can retain more water. It is called the topsoil or the A-horizon. This provides shelter for many living organisms such as worms, rodents, moles and beetles. The roots of small plants are embedded entirely in the topsoil.
- The next layer has a lesser amount of humus but more of minerals. This layer is generally harder and more compact and is called the B-horizon or the middle layer.
- The third layer is the C-horizon, which is made up of small lumps of rocks with cracks and crevices. Below this layer is the bedrock, which is hard and difficult to dig with a spade.
SOIL TYPES
- As you know, weathering of rocks produces small particles of various materials. These include sand and clay. The relative amount of sand and clay depends upon the rock from which the particles were formed, that is the parent rock.
- The mixture of rock particles and humus is called the soil.
- Living organisms, such as bacteria, plant roots and earthworm are also important parts of any soil.
- The soil is classified on the basis of the proportion of particles of various sizes. If soil contains greater proportion of big particles it is called sandy soil. If the proportion of fine particles is relatively higher, then it is called clayey soil. If the amount of large and fine particles is about the same, then the soil is called loamy. Thus, the soil can be classified as sandy, clayey and loamy.
- The sizes of the particles in a soil have a very important influence on its properties. Sand particles are quite large. They cannot fit closely together, so there are large spaces between them. These spaces are filled with air. We say that the sand is well aerated. Water can drain quickly through the spaces between the sand particles. So, sandy soils tend to be light, well aerated and rather dry.
- Clay particles, being much smaller, pack tightly together, leaving little space for air. Unlike sandy soil, water can be held in the tiny gaps between the particles of clay. So clay soils have little air. But they are heavy as they hold more water than the sandy soils.
- The best topsoil for growing plants is loam. Loamy soil is a mixture of sand, clay and another type of soil particle known as silt. Silt occurs as a deposit in river beds. The size of the silt particles is between those of sand and clay. The loamy soil also has humus in it. It has the right water holding capacity for the growth of plants.
PROPERTIES OF SOIL
MOISTURE IN SOIL
- On heating, water in the soil evaporates, moves up and condenses on the cooler inner walls of the upper part of the boiling tube. On a hot summer day, the vapour coming out of the soil reflect the sunlight and the air above the soil seems to shimmer.
SOIL AND CROPS
- Different types of soils are found in different parts of India. In some parts there is clayey soil, in some parts there is loamy soil while in some other parts there is sandy soil.
- Soil is affected by wind, rainfall, temperature, light and humidity. These are some important climatic factors which affect the soil profile and bring changes in the soil structure.
- The climatic factors, as well as the components of soil, determine the various types of vegetation and crops that might grow in any region.
- Clayey and loamy soils are both suitable for growing cereals like wheat, and gram. Such soils are good at retaining water.
- For paddy, soils rich in clay and organic matter and having a good capacity to retain water are ideal.
- For lentils (masoor) and other pulses, loamy soils, which drain water easily, are required.
- For cotton, sandy- loam or loam, which drain water easily and can hold plenty of air, are more suitable.
- Crops such as wheat are grown in the fine clayey soils, because they are rich in humus and are very fertile.
Soil erosion
The removal of land surface by water, wind or ice is known as erosion. Plant roots firmly bind the soil. In the absence of plants, soil becomes loose. So it can be moved by wind and flowing water. Erosion of soil is more severe in areas of little or no surface vegetation, such as desert or bare lands. So, cutting of trees and deforestation should be prevented and effort should be made to increase the green areas.