Nutrition in Human Beings
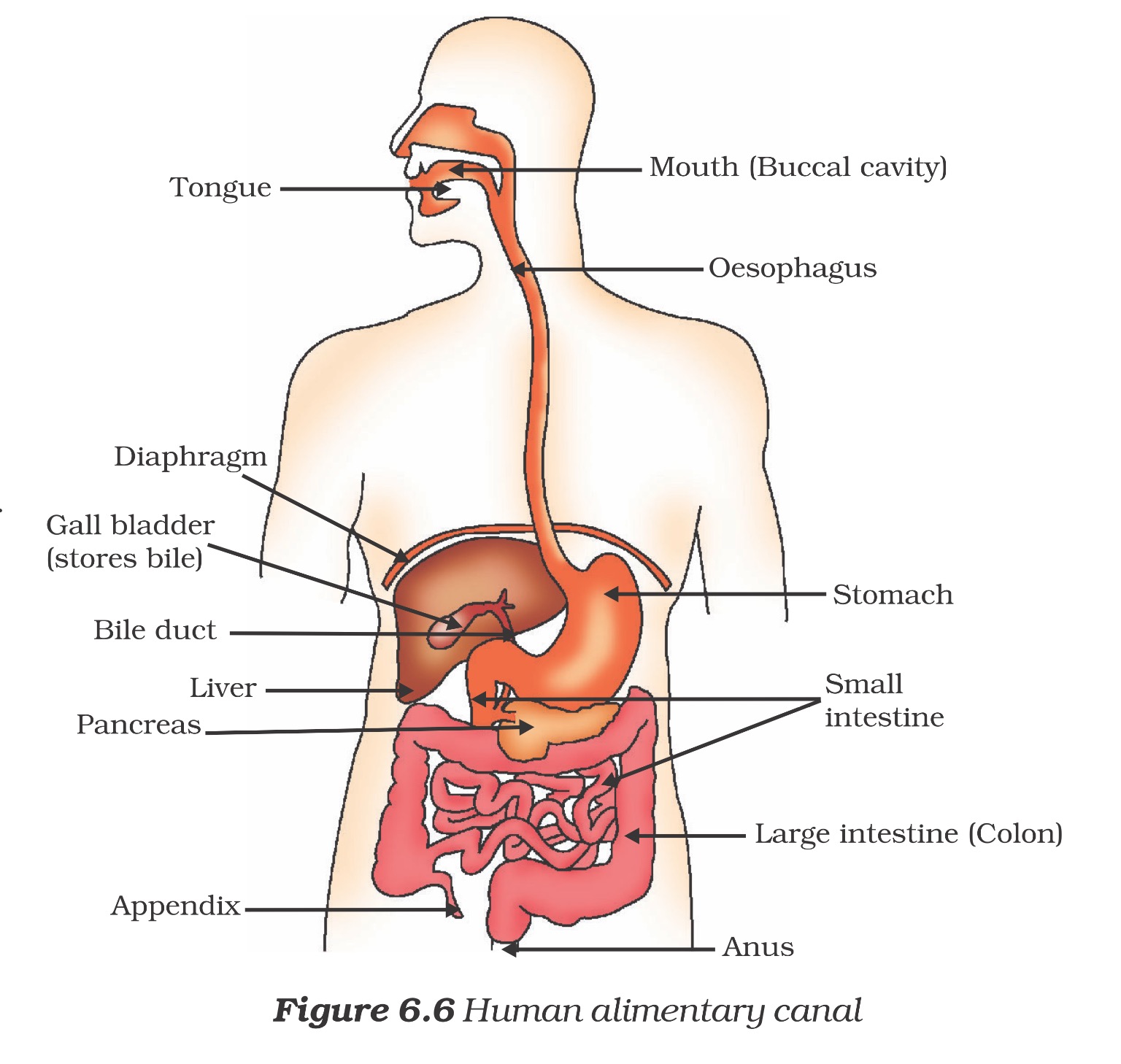
The alimentary canal is basically a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus. We can see that the tube has different parts. Various regions are specialised to perform different functions. What happens to the food once it enters our body? We shall discuss this process here.
- We eat various types of food which has to pass through the same digestive tract.
- Naturally the food has to be processed to generate particles which are small and of the same texture. This is achieved by crushing the food with our teeth.
- Since the lining of the canal is soft, the food is also wetted to make its passage smooth. When we eat something we like, our mouth ‘waters’. This is actually not only water, but a fluid called saliva secreted by the salivary glands.
- Another aspect of the food we ingest is its complex nature. If it is to be absorbed from the alimentary canal, it has to be broken into smaller molecules. This is done with the help of biological catalysts called enzymes.
- The saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase that breaks down starch which is a complex molecule to give sugar.
- The food is mixed thoroughly with saliva and moved around the mouth while chewing by the muscular tongue.
- It is necessary to move the food in a regulated manner along the digestive tube so that it can be processed properly in each part.
- The lining of canal has muscles that contract rhythmically in order to push the food forward. These peristaltic movements occur all along the gut.
- From the mouth, the food is taken to the stomach through the food-pipe or oesophagus.
- The stomach is a large organ which expands when food enters it. The muscular walls of the stomach help in mixing the food thoroughly with more digestive juices.
- These digestion functions are taken care of by the gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach. These release hydrochloric acid, a protein digesting enzyme called pepsin, and mucus.
- The hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium which facilitates the action of the enzyme pepsin.
- The mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of the acid under normal conditions. We have often heard adults complaining about ‘acidity’. Can this be related to what has been discussed above?
- The exit of food from the stomach is regulated by a sphincter muscle which releases it in small amounts into the small intestine.
- From the stomach, the food now enters the small intestine. This is the longest part of the alimentary canal which is fitted into a compact space because of extensive coiling. The length of the small intestine differs in various animals depending on the food they eat.
- Herbivores eating grass need a longer small intestine to allow the cellulose to be digested. Meat is easier to digest, hence carnivores like tigers have a shorter small intestine.
- The small intestine is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. It receives the secretions of the liver and pancreas for this purpose.
- The food coming from the stomach is acidic and has to be made alkaline for the pancreatic enzymes to act. Bile juice from the liver accomplishes this in addition to acting on fats.
- Fats are present in the intestine in the form of large globules which makes it difficult for enzymes to act on them. Bile salts break them down into smaller globules increasing the efficiency of enzyme action. This is similar to the emulsifying action of soaps on dirt.
- The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice which contains enzymes like trypsin for digesting proteins and lipase for breaking down emulsified fats.
- The walls of the small intestine contain glands which secrete intestinal juice. The enzymes present in it finally convert the proteins to amino acids, complex carbohydrates into glucose and fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
- The digested food is taken up by the walls of the intestine. The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption. The villi are richly supplied with blood vessels which take the absorbed food to each and every cell of the body, where it is utilised for obtaining energy, building up new tissues and the repair of old tissues.
- The unabsorbed food is sent into the large intestine where more villi absorb water from this material.
- The rest of the material is removed from the body via the anus. The exit of this waste material is regulated by the anal sphincter.
Note:
Dental caries or tooth decay causes gradual softening of enamel and dentine. It begins when bacteria acting on sugars produce acids that softens or demineralises the enamel. Masses of bacterial cells together with food particles stick to the teeth to form dental plaque. Saliva cannot reach the tooth surface to neutralise the acid as plaque covers the teeth. Brushing the teeth after eating removes the plaque before the bacteria produce acids. If untreated, microorganisms may invade the pulp, causing inflammation and infection.