- Blood transports food, oxygen and waste materials in our bodies. Blood being a fluid connective tissue. Blood consists of a fluid medium called plasma in which the cells are suspended.
- Plasma transports food, carbon dioxide and nitrogenous wastes in dissolved form.
- Oxygen is carried by the red blood cells. Many other substances like salts, are also transported by the blood.
- We thus need a pumping organ to push blood around the body, a network of tubes to reach all the tissues and a system in place to ensure that this network can be repaired if damaged.
Our pump — the heart
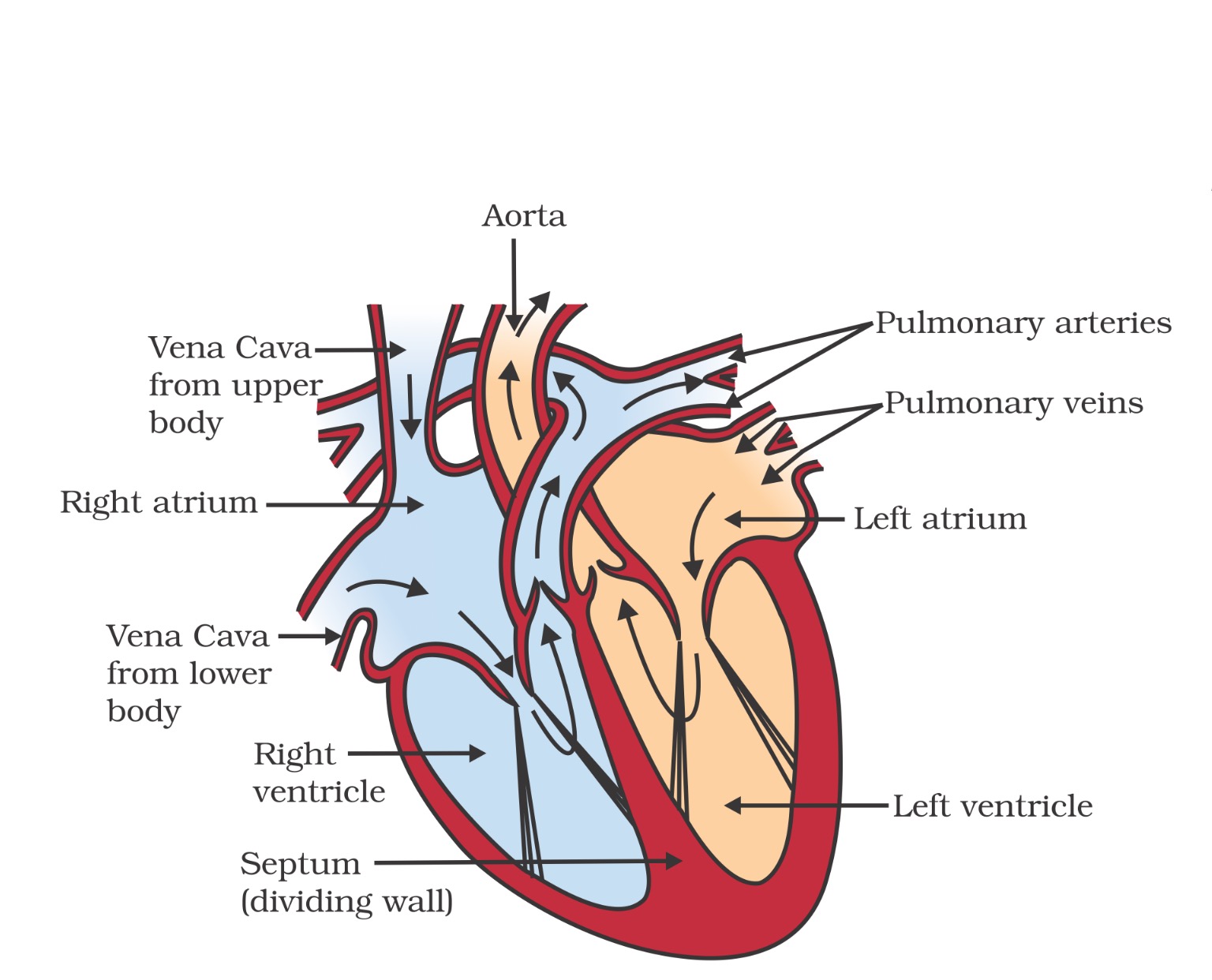
- The heart is a muscular organ which is as big as our fist
- Because both oxygen and carbon dioxide have to be transported by the blood, the heart has different chambers to prevent the oxygen-rich blood from mixing with the blood containing carbon dioxide.
- The carbon dioxide-rich blood has to reach the lungs for the carbon dioxide to be removed, and the oxygenated blood from the lungs has to be brought back to the heart. This oxygen-rich blood is then pumped to the rest of the body.
- We can follow this process step by step (Fig.).
- Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs comes to the thin-walled upper chamber of the heart on the left, the left atrium. The left atrium relaxes when it is collecting this blood.
- It then contracts, while the next chamber, the left ventricle, expands, so that the blood is transferred to it.
- When the muscular left ventricle contracts in its turn, the blood is pumped out to the body.
- De-oxygenated blood comes from the body to the upper chamber on the right, the right atrium, as it expands. As the right atrium contracts, the corresponding lower chamber, the right ventricle, dilates.
- This transfers blood to the right ventricle, which in turn pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation.
- Since ventricles have to pump blood into various organs, they have thicker muscular walls than the atria do.
- Valves ensure that blood does not flow backwards when the atria or ventricles contract.
Oxygen enters the blood in the lungs

- The separation of the right side and the left side of the heart is useful to keep oxygenated and de- oxygenated blood from mixing. Such separation allows a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body.
- This is useful in animals that have high energy needs, such as birds and mammals, which constantly use energy to maintain their body temperature.
- In animals that do not use energy for this purpose, the body temperature depends on the temperature in the environment.
- Such animals, like amphibians or many reptiles have three-chambered hearts, and tolerate some mixing of the oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood streams.
- Fishes, on the other hand, have only two chambers to their hearts, and the blood is pumped to the gills, is oxygenated there, and passes directly to the rest of the body.
- Thus, blood goes only once through the heart in the fish during one cycle of passage through the body.
- On the other hand, it goes through the heart twice during each cycle in other vertebrates. This is known as double circulation.
The tubes – blood vessels
- Arteries are the vessels which carry blood away from the heart to various organs of the body.
- Since the blood emerges from the heart under high pressure, the arteries have thick, elastic walls.
- Veins collect the blood from different organs and bring it back to the heart. They do not need thick walls because the blood is no longer under pressure, instead they have valves that ensure that the blood flows only in one direction.
- On reaching an organ or tissue, the artery divides into smaller and smaller vessels to bring the blood in contact with all the individual cells.
- The smallest vessels have walls which are one-cell thick and are called capillaries. Exchange of material between the blood and surrounding cells takes place across this thin wall.
- The capillaries then join together to form veins that convey the blood away from the organ or tissue.
Maintenance by platelets
- What happens if this system of tubes develops a leak? Think about situations when we are injured and start bleeding.
- Naturally the loss of blood from the system has to be minimised. In addition, leakage would lead to a loss of pressure which would reduce the efficiency of the pumping system.
- To avoid this, the blood has platelet cells which circulate around the body and plug these leaks by helping to clot the blood at these points of injury.
Lymph
- There is another type of fluid also involved in transportation. This is called lymph or tissue fluid.
- Through the pores present in the walls of capillaries some amount of plasma, proteins and blood cells escape into intercellular spaces in the tissues to form the tissue fluid or lymph.
- It is similar to the plasma of blood but colourless and contains less protein.
- Lymph drains into lymphatic capillaries from the intercellular spaces, which join to form large lymph vessels that finally open into larger veins.
- Lymph carries digested and absorbed fat from intestine and drains excess fluid from extra cellular space back into the blood.
Blood pressure
- The force that blood exerts against the wall of a vessel is called blood pressure. This pressure is much greater in arteries than in veins.
- The pressure of blood inside the artery during ventricular systole (contraction) is called systolic pressure and pressure in artery during ventricular diastole (relaxation) is called diastolic pressure.
- The normal systolic pressure is about 120 mm of Hg and diastolic pressure is 80 mm of Hg.
- Blood pressure is measured with an instrument called sphygmomanometer.
- High blood pressure is also called hypertension and is caused by the constriction of arterioles, which results in increased resistance to blood flow. It can lead to the rupture of an artery and internal bleeding.